2026 EU Transport Energy Market Outlook

Trending
Top Posts
Fuel
Turn Fuel Costs into Savings with Expert Fleet Optimization Strategies
7 min read
January 30, 2026
Market Events
How English Language Proficiency Enforcement Will Shape the 2026 Freight Market
5 min read
January 22, 2026
Freight
Reefer Rates Explained: What’s Driving the Trends?
5 min read
January 20, 2026
8 min read
December 23, 2025

Share:
Table of contents
Browse the table of contents to jump straight to the part you’re looking for
Are you confident your fuel surcharge rate is fair and accurate? Fuel surcharge rates are a key component of transportation costs. They’re an additional fee shippers pay carriers to cover the fluctuating cost of fuel. These rates are traditionally included in a fuel surcharge schedule and adjust as diesel prices change.
The problem? Fuel surcharge rates are limited and antiquated. Given the volatility of diesel fuel prices and the constant pressure on profit margins, fuel surcharge rates aren’t accurate enough. This guide will explain fuel surcharge rates and why they don’t cut it in today’s AI-driven world.
Traditional fuel surcharge models, like rate-per-mile tables based on the DOE diesel fuel price index, often result in inaccurate payments due to their reliance on weekly national average data.
These inaccuracies create distortions, leading to overpayment for fuel in some lanes and underpayment in others, whereas a market-based fuel aligns with the actual costs incurred by the carriers on each lane, each day.
Modern, market-based fuel reimbursement strategies offer a more accurate and fair alternative by using real-time, lane-level data that considers the time, price, tax, and geography of each shipment.
Adopting a zero-base rate strategy, which separates fuel costs from linehaul rates, provides further clarity and rewards carriers based on their quality of service.
For decades, the transportation leaders have relied on a few standard methods to calculate fuel surcharges. While once practical, these models now struggle to keep pace with the complexities of modern logistics.
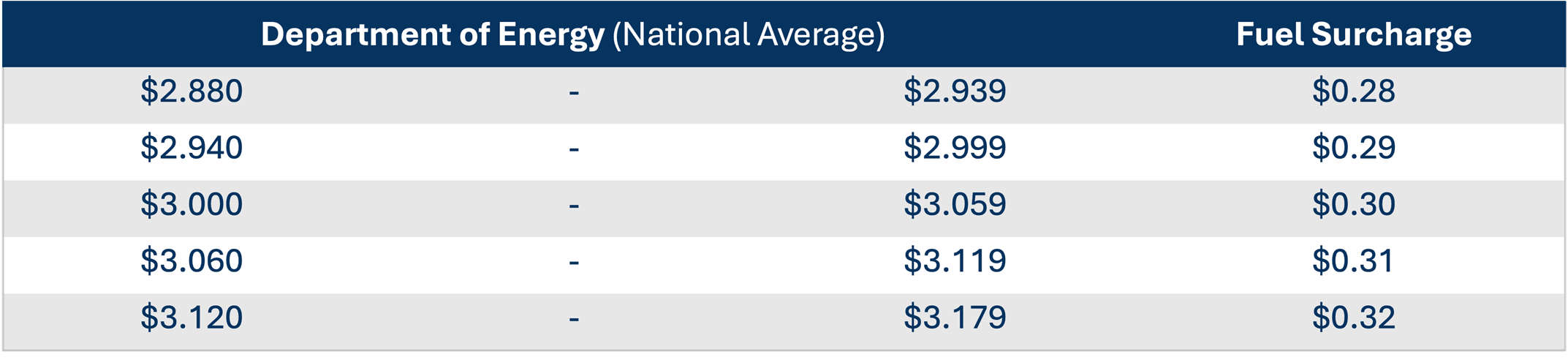
The most common fuel surcharge method uses a rate-per-mile table that references the DOE weekly diesel price index. In this model, the fuel surcharge rate changes based on predetermined price brackets.
For example, a contract might set a base rate of $1.20 per gallon. If the DOE’s average price for the week is $3.121 per gallon, the fuel surcharge schedule will dictate a fuel surcharge rate of $0.32 per mile.
Less common but still in use - some shippers calculate fuel surcharges as a percentage of the linehaul rate. This approach is more efficient but creates greater distortion. Since linehaul rates vary based on factors like service, operational costs, and equipment, tying fuel reimbursement to them disconnects the fuel surcharge from the actual cost of fuel consumed.
Traditional fuel surcharge programs were designed to mitigate risk for carriers. Today, they fail to account for fuel efficiency and consumption, leading to inaccurate charges for shippers. The primary issue is they reference the DOE diesel fuel index, a single national average price, to inform their fuel surcharge rate. Fuel prices can vary dramatically from one state to another due to differences in state taxes and local market dynamics.
Using a national average from the DOE diesel fuel index ignores these geographical variations, creating winners and losers on every lane. A carrier might consistently do business in a high-cost state like California but receive a reimbursement based on the national average, forcing them to absorb the loss. This can lead to carrier pushback, with carriers refusing loads on unprofitable lanes or demanding higher linehaul rates to compensate. Understanding how fuel surcharges hurt your bottom line is the first step toward finding a better solution. Effectively addressing fuel surcharge costs with carriers is crucial for building strong, lasting partnerships.
Fortunately, advancements in technology have enabled more fair and accurate fuel management programs. These modern approaches move away from fuel surcharge rates and toward precise, market-based fuel reimbursement calculations.
A market-based fuel reimbursement program calculates fuel costs based on data that reflects the actual price carriers pay at the pump. This approach considers key variables that traditional fuel surcharge rate models ignore:
Time: Fuel prices change daily, not weekly.
Price: Most well-managed carriers buy fuel at wholesale prices, but the DOE index is based on retail prices.
Taxes: State taxes vary significantly, but a traditional fuel surcharge rate doesn’t consider this component.
Geography: The specific route of the shipment is critical, as diesel prices vary from station to station across the country.
By calculating fuel reimbursements that consider the time, price, tax, and geography of the shipment, shippers can ensure they are paying for the fuel consumed to get their goods to market. This accuracy fosters transparency and strengthens carrier relationships.
To achieve true clarity in transportation costs, many shippers adopt a zero-base rate strategy. This approach separates the cost of fuel from the linehaul rate, which should only reflect the non-fuel costs of moving freight (e.g., driver wages, equipment, and overhead).
With a zero-base strategy, fuel is reimbursed based on market prices, while linehaul rates are negotiated independently. This unbundling of costs allows shippers to manage their fuel management program with precision and gain clear visibility into their total transportation spend.
For organizations looking to manage diesel fuel price volatility, fuel hedging strategies can offer another layer of protection. Hedging allows a shipper to lock in a fuel price for a future period, protecting their budget from unexpected price spikes. When integrated with a market-based fuel management program, hedging provides a powerful tool for controlling and predicting transportation costs.
Selecting the best modern fuel surcharge rate strategy depends on your organization's goals. Key criteria to consider include:
Accuracy: Does the calculation reflect the true cost carriers pay for fuel?
Transparency: Is the calculation clear and easy for both you and your carriers to understand?
Fairness: Does the calculation treat all parties equitably?
Scalability: Can the fuel management program support your transportation network as it grows?
Integration: Can it integrate with your existing data processes?
If your current fuel management program lacks transparency, it’s time to consider an update. Look for partners and tools that calculate real-time, market-based fuel reimbursements.
Fuel Recovery addresses the weaknesses of traditional fuel surcharge models. We replace national averages with real-time, lane-level calculations based on the time, price, tax, and geography of the shipment. By leveraging daily, lane-level data, we determine a fair and accurate fuel reimbursement.
This approach eliminates distortions caused by national indices and ensures shippers pay for the fuel their freight actually consumes, and carriers are compensated fairly for the prices they pay.
The transportation industry is rapidly evolving, and fuel surcharge rates are no exception. AI and predictive analytics will enable even more dynamic pricing and reimbursement models, as well as emission tracking. This will provide a complete picture of a shipment’s total cost and emissions footprint, empowering shippers to make strategic decisions that benefit both their budget and their sustainability initiatives. The industry is also moving toward holistic linehaul rate and fuel cost modeling, where every component of transportation spend is visible, manageable, and optimized.
Relying on a traditional fuel surcharge rate is no longer a viable strategy for managing a volatile and significant expense. Effectively managing fuel surcharge rates is about building a more resilient, transparent, and sustainable transportation network strategy. By embracing market-based fuel reimbursement strategies, you can eliminate inaccuracies, strengthen carrier partnerships, and gain greater control over your transportation spend.
A fuel surcharge rate is typically calculated using a rate-per-mile table tied to the DOE's weekly diesel price index. While widely used, this method is inaccurate because it doesn't account for lane-level price differences, leading to over or underpayments.
To calculate a fuel surcharge, you first determine the average diesel fuel price for a given week from a source like the DOE diesel fuel price index. You then find the corresponding rate-per-mile on your agreed-upon surcharge schedule and multiply that rate by the number of miles for the shipment. A more modern and accurate method involves partnering with a provider like Breakthrough to calculate a market-based price for the actual fuel consumed on a specific lane.
An effective fuel surcharge rate model should be influenced by factors that reflect the true cost of fuel. These include the price carriers pay for fuel, the geographic location of the route (including state taxes), the truck’s fuel efficiency (MPG), and the distance of the trip. Relying on these variables, rather than a single national average, creates a fair and accurate reimbursement.
Index-based surcharges, which often rely on a national average like the DOE, overpay carriers because they don’t reflect the true cost of fuel and fail to account for fuel efficiency improvements from newer equipment. A carrier often operates a more fuel-efficient truck than the 6.0 MPG standard used in calculations or travel through states with lower fuel costs. In these cases, a fuel surcharge based on a national average and an inefficient MPG standard results in the shipper paying more than the actual fuel cost.
Fuel Recovery
Discover how to calculate market-based fuel reimbursements and overcome the limits of traditional fuel surcharge models.


7 min read
January 30, 2026
Maximize performance with proven fleet optimization strategies. Learn how to manage driver compliance and leverage expanding fuel margins for real savings.
Read more
5 min read
January 22, 2026
Stricter English Language Proficiency rules are impacting driver capacity. See our data on how this is leading to upward linehaul rate pressure in 2026.
Read more
5 min read
January 20, 2026
Understand the latest trends in reefer rates. Our data analysis dissects if the market is in a seasonal swing or facing a true inflection point.
Read more